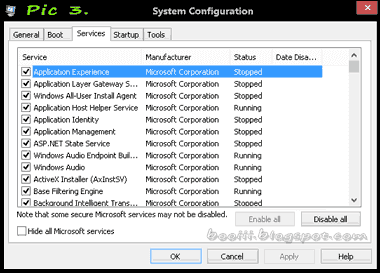
Safe mode is a troubleshooting option for Windows that starts your computer in a limited state. Only the basic files and drivers necessary to run Windows are started. The words Safe Mode appear in the corners of your monitor to identify which Windows mode you're using. Safe mode is a troubleshooting option for Windows that starts your computer in a limited state. Only the basic files and drivers necessary to run Windows are started. The words Safe Mode appear in the corners of your monitor to identify which Windows mode you're using.
If an existing problem doesn't reappear when you start in safe mode, you can eliminate the default settings and basic device drivers as possible causes. If you don't know the cause of the problem, you can use the process of elimination to help you find the problem. Try starting all of the programs you commonly use, including the programs in your Startup folder, one by one to see if a program might be the cause of the problem.
If your computer automatically starts in safe mode without prompting, a problem with your computer might be preventing Windows from starting normally. If you think the cause of the problem might be a recently installed program or device, try using Recovery in Control Panel.
Start your computer in safe mode
1. Remove all floppy disks, CDs, and DVDs from your computer, and then restart your computer. Click the Start button , click the arrow next to the Shut Down button , and then click Restart.
 Do one of the following: Do one of the following:
1. If your computer has a single operating system installed : press and hold the F8 key as your computer restarts. You need to press F8 before the Windows logo appears. If the Windows logo appears, you'll need to try again by waiting until the Windows logon prompt appears, and then shutting down and restarting your computer.
2. If your computer has Multi OS installed(Windows 7 Boot Loarder)
: use the arrow keys to highlight the operating system you want to start in safe mode, and then press F8.
- On the Advanced Boot Options screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the safe mode option you want, and then press Enter.
Advanced Boot Options (including safe mode)
The Advanced Boot Options screen lets you start Windows in advanced troubleshooting modes. You can access the menu by turning on your computer and pressing the F8 key before Windows starts.
Some options, such as safe mode, start Windows in a limited state, where only the bare essentials are started. If a problem doesn't reappear when you start in safe mode, you can eliminate the default settings and basic device drivers and services as possible causes. Other options start Windows with advanced features intended for use by system administrators and IT professionals. For more information, go to the Microsoft website for IT professionals.
1. Repair Your Computer
Shows a list of system recovery tools you can use to repair startup problems, run diagnostics, or restore your system. This option is available only if the tools are installed on your computer's hard disk. If you have a Windows installation disc, the system recovery tools are located on that disc.
2. Safe Mode
Safe mode is a troubleshooting option for Windows that starts your computer in a limited state. Only the basic files and drivers necessary to run Windows are started. The words Safe Mode appear in the corners of your monitor to identify which Windows mode you're using.
If an existing problem doesn't reappear when you start in safe mode, you can eliminate the default settings and basic device drivers as possible causes. If you don't know the cause of the problem, you can use the process of elimination to help you find the problem. Try starting all of the programs you commonly use, including the programs in your Startup folder, one by one to see if a program might be the cause of the problem.
If your computer automatically starts in safe mode without prompting, a problem with your computer might be preventing Windows from starting normally. If you think the cause of the problem might be a recently installed program or device, try using Recovery in Control Panel
 3. Safe Mode with Networking 3. Safe Mode with Networking
Starts Windows in safe mode and includes the network drivers and services needed to access the Internet or other computers on your network.
4. Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Starts Windows in safe mode with a command prompt window instead of the usual Windows interface. This option is intended for IT professionals and administrators.
5. Enable Boot Logging
Creates a file, ntbtlog.txt, that lists all the drivers that are installed during startup and that might be useful for advanced troubleshooting.
6. Enable low-resolution video (640×480)
Starts Windows using your current video driver and using low resolution and refresh rate settings. You can use this mode to reset your display settings.
7. Last Known Good Configuration (advanced)
Starts Windows with the last registry and driver configuration that worked successfully.
8. Directory Services Restore Mode
Starts Windows * domain controller running *Active Directory so that the directory service can be restored. This option is intended for IT professionals and administrators.
* domain controller : A server in an active directory network that manages user logon and access to net work and shared resources.
* Active Directory : Awindows based directory service that stores information about resources (sush as printer, users,computer& groups) and makes this information available to users and other omputers.
|
9. Debugging Mode
Starts Windows in an advanced troubleshooting mode intended for IT professionals and system administrators.
10. Disable automatic restart on system failure
Prevents Windows from automatically restarting if an error causes Windows to fail. Choose this option only if Windows is stuck in a loop where Windows fails, attempts to restart, and fails again repeatedly.
 11. Disable Driver Signature Enforcement 11. Disable Driver Signature Enforcement
Allows drivers containing improper signatures to be installed.
12. Start Windows Normally
Starts Windows in its normal mode.
13. Description(Current Select) , 14. select ENTER = Choose , 15. select ESC = Cancel
|